Appearance
CUBE XCC Call Details
The Call Details page provides comprehensive information about individual calls processed through your Cisco CUBE XCC integration. This detailed view allows you to analyze call quality, troubleshoot issues, and gain insights into your voice communications at the individual call level.
Feature Overview
The CUBE XCC Call Details page offers:
- Comprehensive Call Records: View detailed information for each call including timestamps, caller/called numbers, quality metrics, and call attributes
- Advanced Filtering: Quickly find specific calls using search and filter capabilities
- Quality Metrics Analysis: Analyze MOS scores, packet loss, and round-trip time for each call
- Call Attribute Tracking: Monitor call direction, duration, codec usage, and policy actions
- Troubleshooting Tools: Identify problematic calls and diagnose communication issues
- Data Export: Export call records for further analysis or reporting
Feature Requirements
- Call Telemetry Server Appliance 0.8.4 or later
- Call Telemetry Advanced License
- Configured CUBE XCC Integration
- Add Disconnect Events to your CUBE XCC integration to enable quality reporting
Accessing Call Details
To access the CUBE XCC Call Details page:
- Log in to your Call Telemetry dashboard
- Navigate to Analytics > CUBE XCC Call Details
- Use the time period selectors to view calls within a specific timeframe
Time Period Selection
The dashboard allows you to select different time periods for data analysis:
- 1 Hour: View the most recent hour of call data
- 24 Hours: View the last 24 hours (default view)
- 7 Days: View the last week of call data
- 30 Days: View the last month of call data
- Custom: Select a custom date and time range
Timezone Selection
The dashboard displays all times in your selected timezone. You can change the timezone by clicking on the timezone dropdown in the top-right corner of the page.
Call Details Table
The Call Details table provides a comprehensive view of individual calls with the following information:
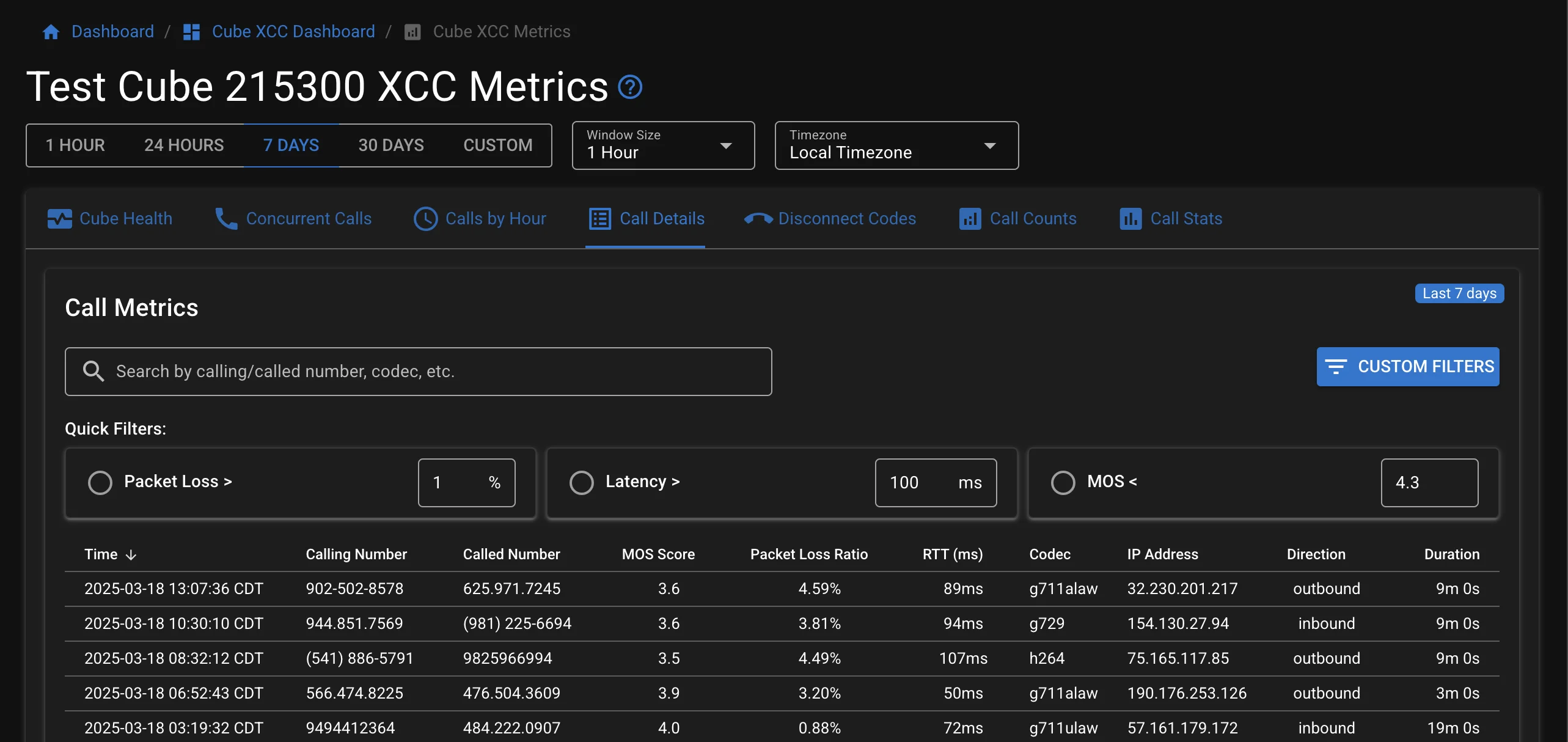
Table Columns
- Connected At: Timestamp when the call was established
- Disconnected At: Timestamp when the call ended
- Cube: The CUBE device that processed the call
- Call ID: Unique identifier for the call
- Connection ID: Unique identifier for the connection
- Calling Number: The originating phone number
- Called Number: The destination phone number
- MOS Score: Mean Opinion Score indicating call quality (1-5 scale)
- Packet Loss Ratio: Percentage of lost packets during the call
- RTT (ms): Round Trip Time in milliseconds
- MOS Score: Mean Opinion Score indicating call quality (1-5 scale)
- Packet Loss Ratio: Percentage of lost packets during the call
- RTT (ms): Round Trip Time in milliseconds
Additional Call Attributes
- Codec: Audio codec used for the call (e.g., G.711, G.729, Opus) - helps identify potential quality or compatibility issues
- Peer IP: IP address of the peer device - useful for network troubleshooting and identifying problematic endpoints
- Direction: Call direction (inbound or outbound) - helps analyze traffic patterns and troubleshoot one-way issues
- Duration: Call duration in seconds - useful for identifying abnormally short calls that may indicate connection problems
- Action Taken: The policy action taken for the call (e.g., allow, block) - helps verify policy enforcement
The table can be sorted by any column by clicking on the column header.
Search and Filtering
The Call Details page offers powerful search and filtering capabilities to help you find specific calls:
Quick Search
Use the search bar at the top of the table to search by:
- Calling or called number
- Codec information
- Call ID or Connection ID
Quick Filters
Apply quick filters to focus on calls with specific quality metrics:
- Packet Loss >: Filter calls with packet loss greater than a specified percentage
- Latency >: Filter calls with RTT greater than a specified value (ms)
- MOS <: Filter calls with MOS score less than a specified value
Custom Filters
Click the CUSTOM FILTERS button to access advanced filtering options:
- Select the field to filter on (e.g., Calling Number, Called Number, MOS Score)
- Choose the operator (equals, contains, greater than, less than, etc.)
- Enter the filter value
- Add multiple filters to create complex queries
- Apply filters to update the table view
Data Export
Export your call details data for further analysis or reporting:
- Apply any desired filters to the call details table
- Click the EXPORT CSV button in the top-right corner
- The system will generate a CSV file containing all visible call records
- Save the file to your local system for further analysis
Using Call Details for Troubleshooting
The Call Details page is a powerful tool for troubleshooting voice communication issues. Finding troubled calls quickly is essential for maintaining high-quality voice communications and resolving issues before they affect user experience:
Identifying Problem Calls
- Sort by MOS Score (ascending) to find the lowest quality calls
- Sort by Packet Loss Ratio (descending) to find calls with the highest packet loss
- Sort by RTT (descending) to find calls with the highest latency
Analyzing Patterns
- Filter by specific calling or called numbers to identify user-specific issues
- Filter by time ranges to identify time-based patterns
- Filter by CUBE to identify device-specific issues
Correlating with Network Issues
- Compare call quality metrics with network performance data
- Identify patterns in call quality degradation that may correlate with network events
- Use timestamp information to align with other system logs
Interpreting Call Quality Metrics
Voice quality is influenced by multiple factors that can be measured and analyzed through the Call Details page. Understanding these metrics helps you identify the root cause of call quality issues:
MOS Score (Mean Opinion Score)
MOS is a numerical measure of the perceived quality of voice communications:
- 5.0: Perfect quality, imperceptible impairments
- 4.0-5.0: Excellent quality
- 3.5-4.0: Good quality
- 3.0-3.9: Fair quality, perceptible but not annoying
- 2.0-2.9: Annoying and objectionable
- Below 2.0: Very annoying and objectionable
Network Quality Indicators
Network quality significantly impacts voice communications. The Call Details page provides key network metrics:
Packet Loss Ratio
Packet loss occurs when data packets fail to reach their destination, causing gaps in audio:
- Low packet loss (0-2%): Generally acceptable for voice communications
- Moderate packet loss (2-5%): May cause noticeable quality degradation
- High packet loss (>5%): Likely to cause significant call quality issues
RTT (Round Trip Time)
RTT measures network latency, affecting conversation flow and causing echo or talk-over issues:
- Low latency (<100ms): Excellent for voice communications
- Moderate latency (100-300ms): Acceptable but may cause slight conversation delays
- High latency (>300ms): Problematic for interactive voice communications
Troubleshooting Common Issues
The Call Details page is your primary tool for identifying and resolving voice quality issues. Here's how to approach common problems:
General Network Quality Issues
When calls show poor quality metrics (low MOS, high packet loss, high RTT):
- Check network infrastructure: Verify switches, routers, and firewalls are properly configured
- Examine QoS settings: Ensure voice traffic is properly prioritized across the network
- Review bandwidth allocation: Verify sufficient bandwidth is available for voice traffic
- Check for network congestion: Look for competing traffic that may impact voice quality
- Verify WAN performance: For calls traversing WAN links, check link quality and utilization
Codec and Media Issues
When specific calls show quality problems:
- Check codec compatibility: Verify endpoints support the negotiated codec
- Review transcoding points: Identify where transcoding occurs and potential quality impact
- Examine media path: Verify direct media path between endpoints when possible
- Check for one-way audio: Use direction and peer IP information to troubleshoot media flow
Pattern-Based Troubleshooting
Use the Call Details page to identify patterns in troubled calls:
- Time-based patterns: Filter by time to identify issues during specific periods
- User-based patterns: Filter by calling/called numbers to identify user-specific issues
- Location-based patterns: Use peer IP to identify location-specific problems
- Device-based patterns: Filter by CUBE to identify device-specific issues