Appearance
PostgreSQL CRM Database for Cisco CallManager Caller ID
Overview
Transform your Cisco phone system into a customer-aware communication platform by connecting PostgreSQL databases to display caller names in real-time. When customers call, their name can appear on agent phones instantly - pulled directly from your CRM, student information system, or custom database.
This PostgreSQL integration executes SQL queries during incoming calls to retrieve caller information and display it on Cisco IP phones, replacing generic phone numbers with meaningful customer names.
Why Use PostgreSQL for Caller ID
- Instant Customer Recognition: Agents see customer names before answering
- Any SQL Database: Works with existing CRM, ERP, or custom databases
- Real-time Lookups: Queries execute during the call
- Zero Phone Changes: Works with all Cisco IP phone models
📹 Watch our PostgreSQL CRM Integration Video Tutorial
Feature Requirements
- Call Telemetry Appliance 0.7.0 or later
- Call Telemetry Premium License
- Cisco Callmanager 8.5 with CURRI API Integration to Call Telemetry
- Configured External Call Control Profile Inspection - A route pattern, translation pattern, or phone extension must be enabled for Call Telemetry Policy inspection. If Call Telemetry is not inspecting the call, it will not be able to see the ip phone call history.
Configuration Overview
Setting up PostgreSQL caller ID takes about 10 minutes:
- Create a policy rule to intercept incoming calls
- Configure PostgreSQL connection and SQL query
- Map database results to caller ID display
- Test the call
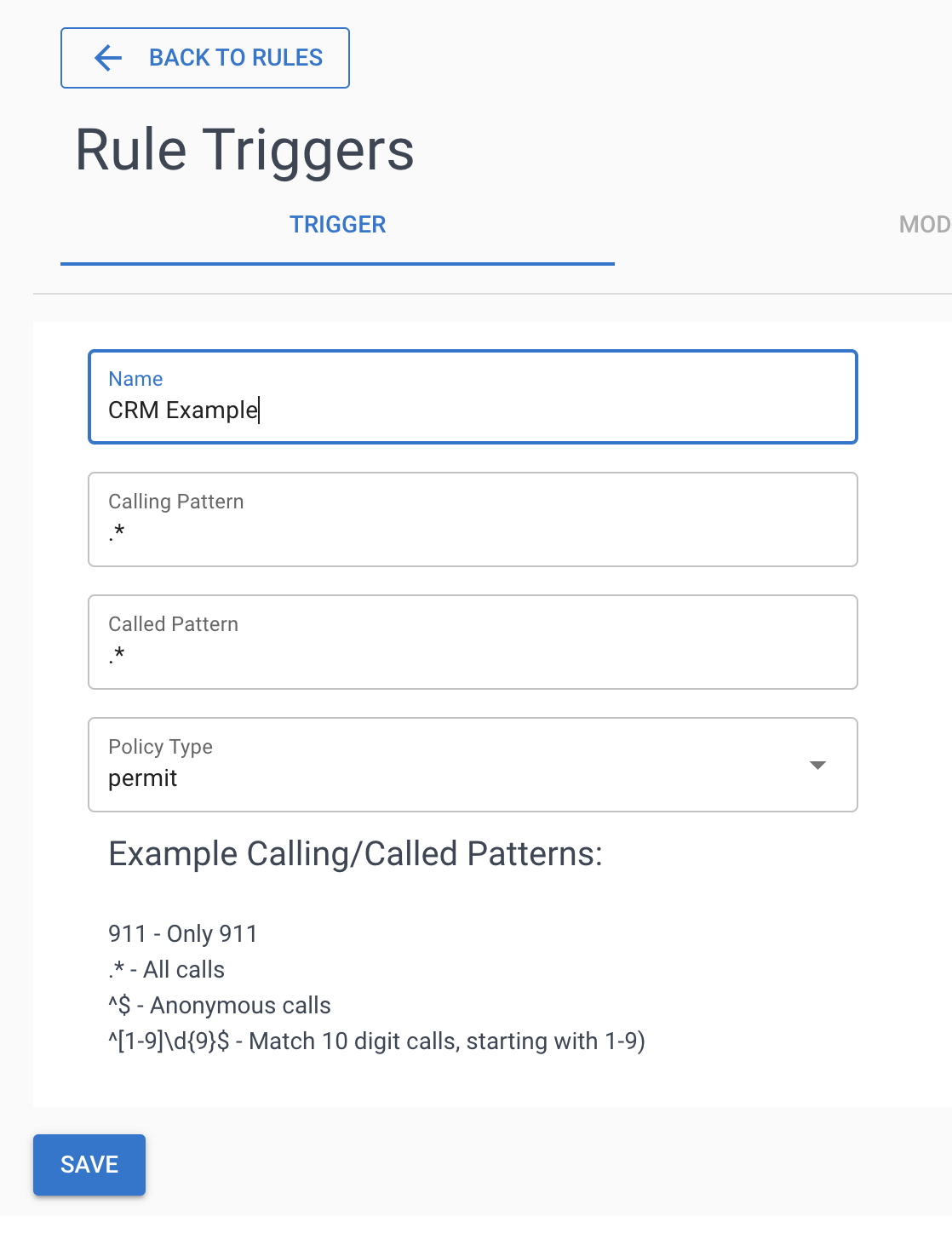
Step 1: Create Call Policy and Rule
First, set up a policy to intercept incoming calls for CRM lookup.
Quick Setup
- Navigate to Policies → Add Policy
- Name it "CRM Lookup Policy"
- Add a rule with trigger pattern
.*to match all calls - Or use specific patterns like
408.*for area codes
Verify Policy is Active
Your policy should show "Registered" status and accumulate hits as calls arrive. Check Call Policy History to confirm it's working.
📚 New to policies? See Policy Configuration Guide and Rule Triggers Guide
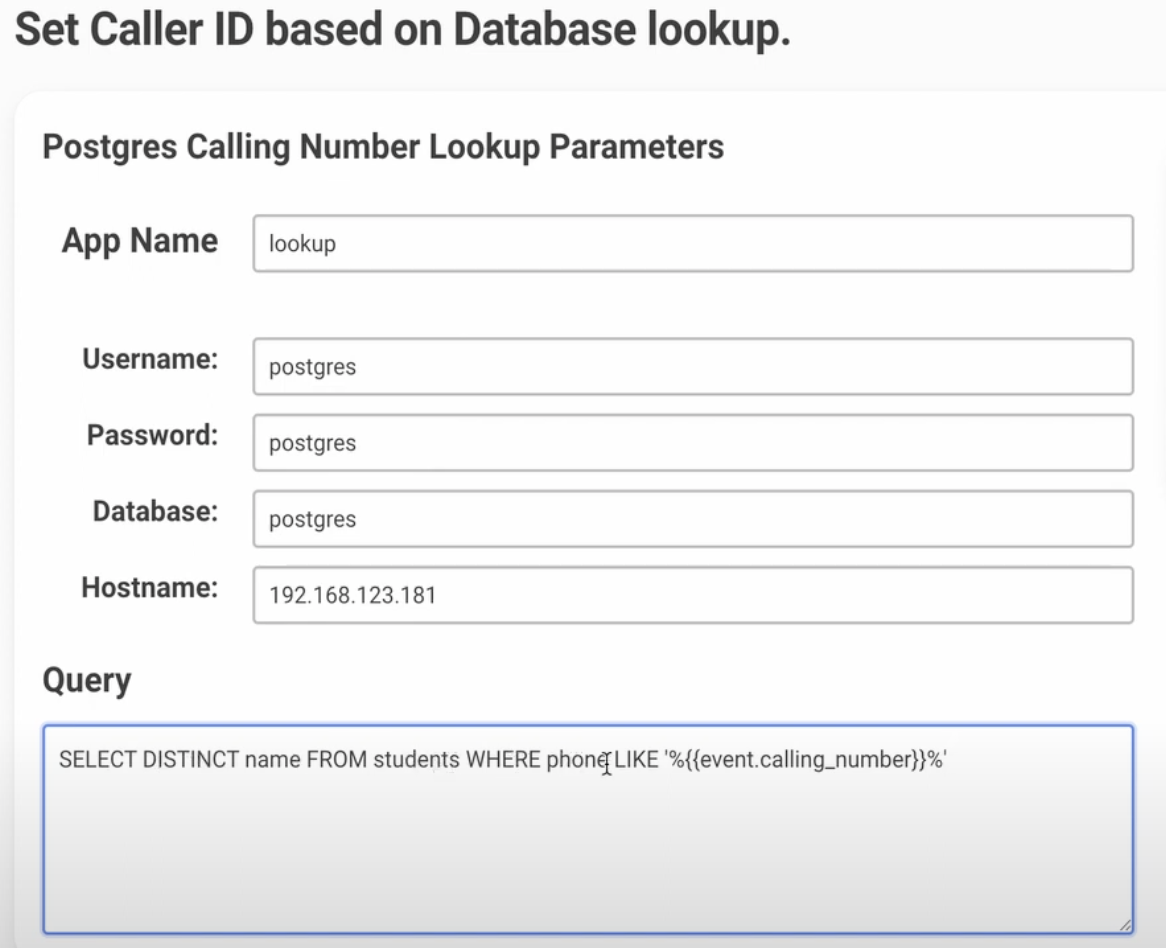
Step 2: Configure PostgreSQL Database Connection
Create the PostgreSQL App
- Go to Realtime Policies → Apps
- Click Add → Select PostgreSQL (under Realtime tab)
- Configure your database connection:
Connection String Format:
host=yourserver.com dbname=customerdb user=readonly password=secretpassSQL Query Requirements:
- Must return exactly one value (the name to display)
- Use
{event.calling_number}for the caller's phone number - Test your query directly in PostgreSQL first
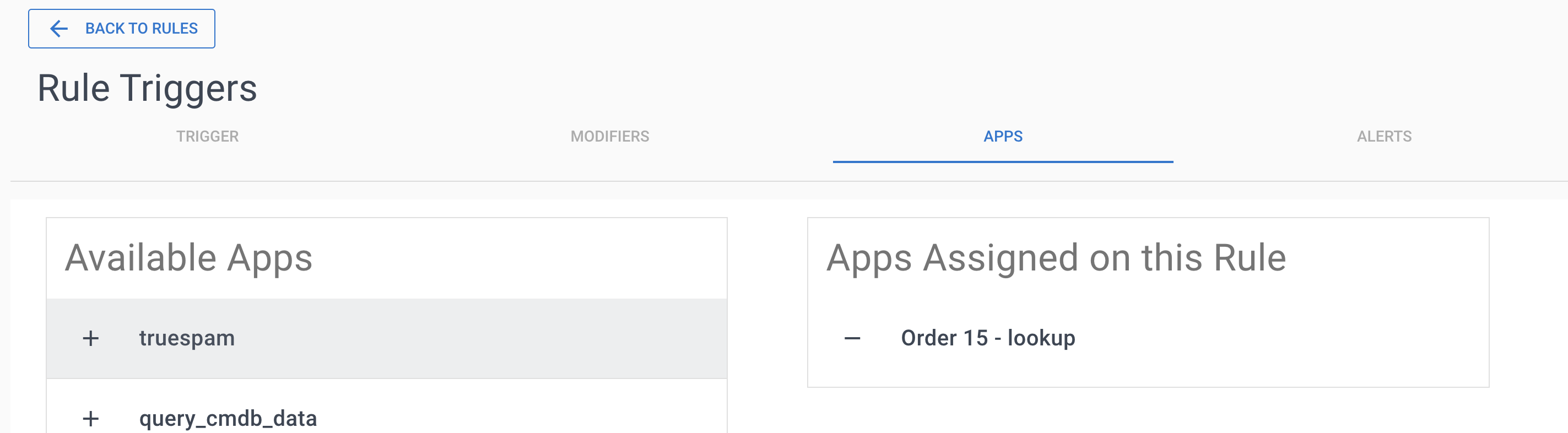
Step 3: Associate PostgreSQL App with Your Rule
- Open your CRM Policy and select the rule
- Click the + button next to your PostgreSQL App
- The app now executes for every matching call
Step 4: Test Database Query Results
Use Call Tests to verify your PostgreSQL query returns the expected customer name:
- Navigate to Policies -> Call Test
- Enter a test calling number that exists in your database
- Run the test and check
app_data.lookup.data.results
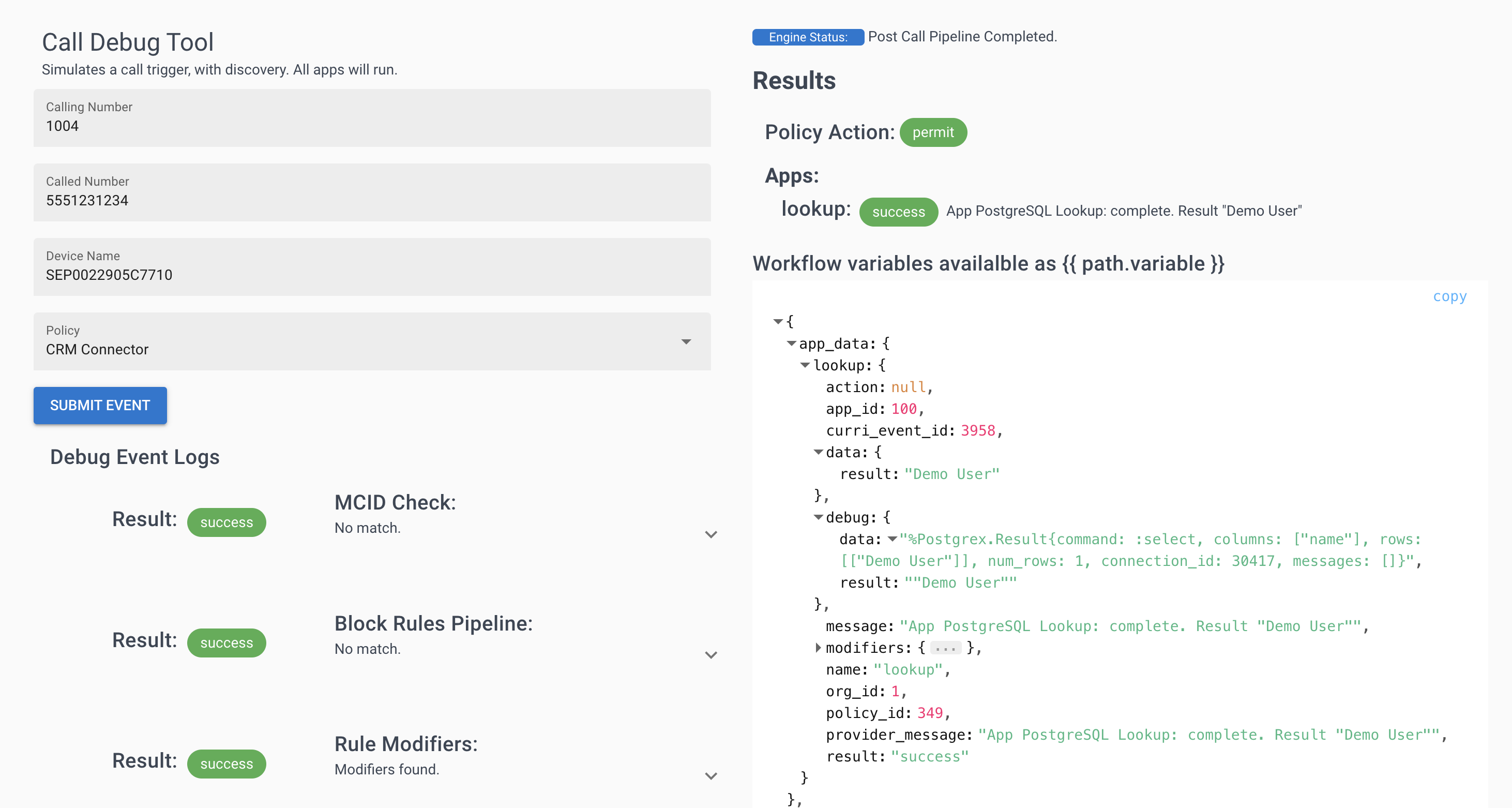
✅ Success: You should see the customer name returned from your database
Step 5: Display Customer Name on Phones
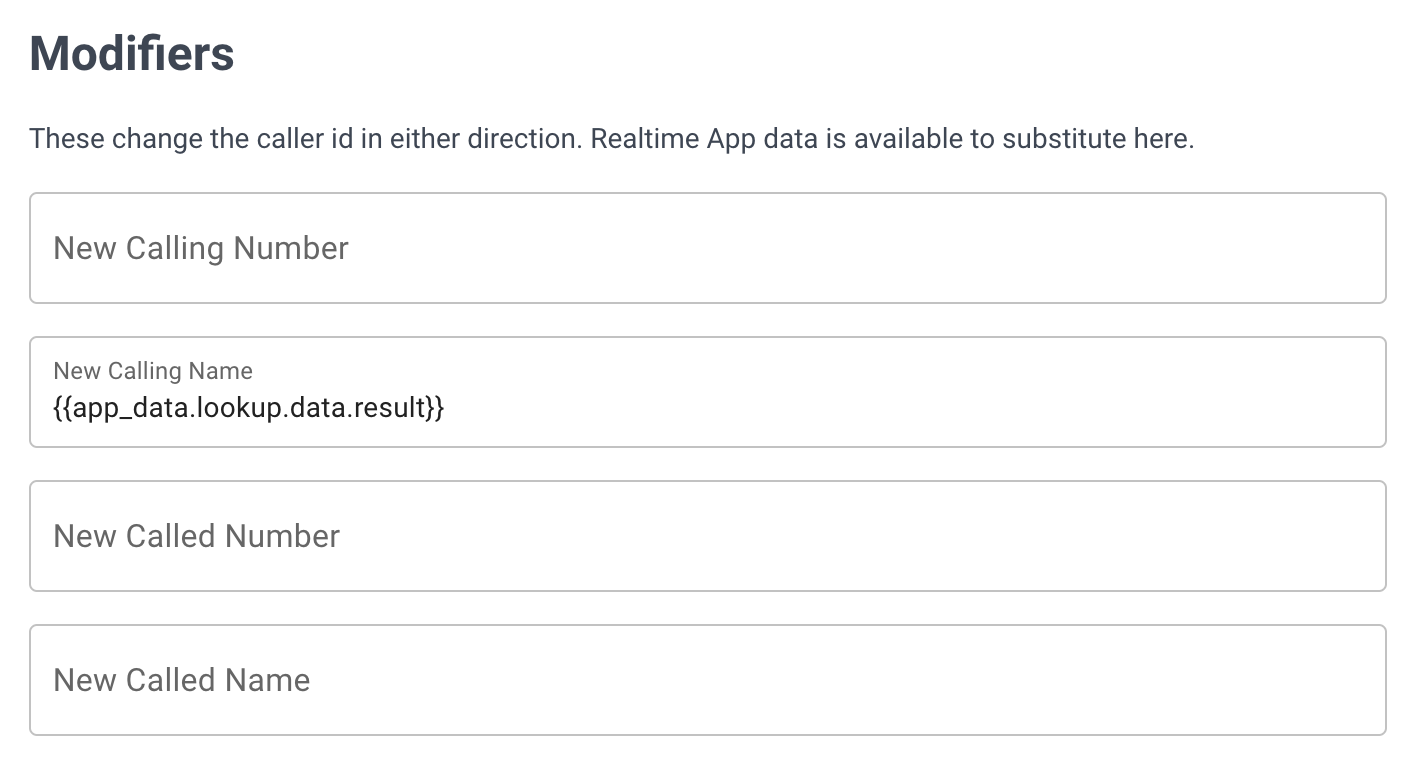
Map the database result to the caller ID display:
- In your rule, find the Calling Party Name field
- Enter:
{app_data.lookup.data.results} - Save the rule
Now when customers call, their name from PostgreSQL replaces the phone number on agent displays.
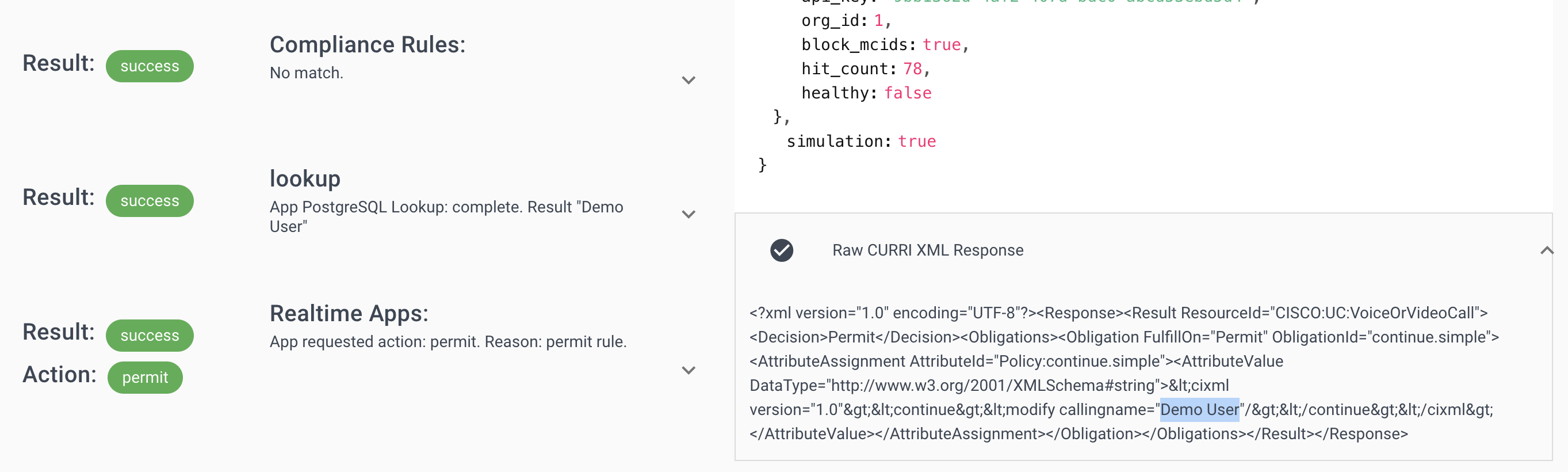
Step 6: Verify Caller ID Display
Confirm the integration works end-to-end:
- Run another call test with a known customer number
- Check the CURRI API response (right panel)
- Verify
calling_nameshows your database value - Make a real test call to see the name on phones
Troubleshooting
No name displayed?
- Verify phone number format matches database (with/without country code)
- Check PostgreSQL user has SELECT permissions
- Test query directly in psql or pgAdmin
- Review Call Test results for error messages
Connection errors?
- Verify network connectivity from Call Telemetry to PostgreSQL
- Check firewall rules allow port 5432
- Confirm connection string format is correct