Appearance
Call Telemetry Cluster and High Availability Deployment Guide
This guide provides detailed instructions for setting up and deploying the Call Telemetry application using Kuberenetes with load balancing an a HA PostgreSQL Cluster.
Supported Deployments
- Onprem: Call Telemetry uses K3s.io A lightweight Kubernetes distribution designed for easy installation and operation of Kubernetes.
- Cloud: Any cloud provider that supports Kubernetes. Our preferred providers with deployments are Digital Ocean, AWS, an Azure.
Deployment and Version Control
Helm Charts and Helmfile manifests manage the deployment of the Call Telemetry application. This allows us to easily manage and version control the deployment process.
Our Deployment and Charts are in the Call Telemetry K8S Charts repository.
Support
Kubernetes Clustering is free to use on your own, but no support is provided without a paid support license. Please contact Support for more information.
Benefits
- High Availability: The cluster is designed to be highly available, with multiple nodes and load balancing.
- Scalability: The cluster can be easily scaled up or down as needed.
- Flexibility: The cluster can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, making it easy to adapt to different environments.
- Prod and Dev: The cluster can have multiple environments, such as production and development, running on the same cluster. This can be helpful for testing and development purposes.
High-Level Cluster Isolation Diagram
The diagram above illustrates the high-level isolation between environments in the Call Telemetry Kubernetes cluster. Key points:
- Isolated Environments: ct-dev and ct-prod are completely isolated from each other
- Virtual IPs: Each environment has its own dedicated virtual IP address
- Shared Infrastructure: MetalLB is the only shared component, providing load balancing services to both environments
Architecture
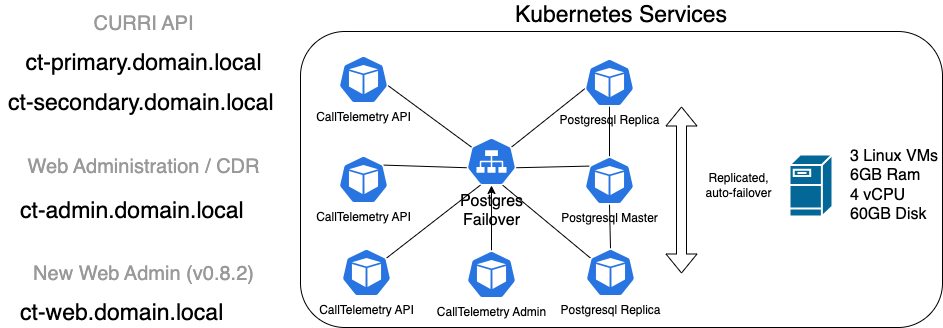
Deployment Components
- Node IPs: 3 Nodes are reocmmended for a highly available cluster.
- Virtual IP: A virtual IP address for the cluster. This is used for load balancing and failover. We use MetalLB for this.
- PostgreSQL Operator: The CrunchyData PostgreSQL Operator automates PostgreSQL HA database cluster deployment, management, and monitoring in Kubernetes.
Installation Steps
OS Preparation
This step configures the firewall, and installs some tools needed for running Kubernetes.
Supported OS Versions
- AlmaLinux 9.x
- RHEL 9.x
- CentOS Stream 9.x
bash
sudo curl https://get.calltelemetry.com | sudo sh -s -- prep-cluster-nodeK3s Installation
K3s is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution designed for easy installation and operation of Kuberenetes.
Setting Up the Primary Node
Install K3s Install K3s on the primary node. Note the token value, which is hashed into the shared cluster secret value.
bash# From Primary Node. export K3S_TOKEN="calltelemetry" curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_KUBECONFIG_MODE=0644 sh -s server --cluster-init --disable traefik --disable servicelbThis command initializes the K3s server, disables Traefik (a default ingress controller), and the default service load balancer.
Configure Kubectl Set up
kubectl, the command-line tool for interacting with the Kubernetes cluster:bash# From Primary node. mkdir -p ~/.kube sudo cat /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml > ~/.kube/config
Optionally Setting Up Secondary Nodes
3 Nodes is typical for a Kubenretes cluster, but you can skip this step and just run a single node.
Install K3s on Secondary Nodes Join secondary nodes to the K3s cluster. Note the token value, and the primary node IP address.
bash# From the secondary node to be installed. export primary_ip="192.168.123.156" export K3S_TOKEN="calltelemetry" sudo curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_URL="https://$primary_ip:6443" K3S_KUBECONFIG_MODE=0644 sh -s server --disable traefik --disable servicelb mkdir -p ~/.kube sudo cat /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml > ~/.kube/configChecking Nodes
bash# From any node. [calltelemetry@ct-node-1 ~]$ kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ct-node-1 Ready control-plane,etcd,master 34h v1.29.6+k3s2 ct-node-2 Ready control-plane,etcd,master 33h v1.29.6+k3s2 ct-node-3 Ready control-plane,etcd,master 34h v1.29.6+k3s2 [calltelemetry@ct-node-1 ~]$Scale DNS Pods Adjust DNS pod replicas to match the number of total nodes. This helps with failover.
bash# From any node. kubectl scale deployment.v1.apps/coredns --replicas=3 -n kube-systemCheck DNS Pod Scale
bash# From any node. [calltelemetry@ct-node-1 ~]$ kubectl get pods -A | grep dns kube-system coredns-6799fbcd5-2v68f 1/1 Running 0 13m kube-system coredns-6799fbcd5-55mdh 1/1 Running 0 13m kube-system coredns-6799fbcd5-6skkc 1/1 Running 2 (<invalid> ago) 34h [calltelemetry@ct-node-1 ~]$
Applicaton Deployment
Our deployment is managed by Helm and Helmfile. Instructions are in the [Call Telemetry K8S Charts repository](
Kubernetes Cluster Setup
Troubleshooting
Uninstall K3s
To uninstall K3s, use:
bash
# Node to be uninstalled.
/usr/local/bin/k3s-uninstall.sh